Superfetch is a feature in Windows operating systems that aims to improve system performance by preloading frequently used applications into memory. While this feature can provide benefits such as faster application launches and smoother multitasking, it has also been the subject of debate among computer users.
One of the main arguments in favor of disabling Superfetch is that it can consume a significant amount of system resources, particularly on systems with limited RAM. By preloading applications into memory, Superfetch can occupy a large portion of available RAM, leaving less space for other processes. This can lead to increased disk and CPU usage, potentially slowing down the system as a whole.
On the other hand, proponents of Superfetch argue that the feature is designed to adapt to the user’s usage patterns and optimize system performance accordingly. Superfetch learns from the user’s behavior and prioritizes the loading of frequently used applications, ensuring that they are always readily available for quick access.
Furthermore, Superfetch is particularly beneficial for users with mechanical hard drives. The feature can reduce disk I/O operations by caching frequently used data, leading to improved disk performance and faster application launches.
What is Superfetch and How Does It Work?
Superfetch is a feature in Windows operating systems that is designed to improve system performance. It works by analyzing the way you use your computer and predicting which applications and files you are likely to use in the future. Superfetch then preloads these files and applications into your computer’s memory (RAM) so that they can be accessed more quickly when needed.
Superfetch monitors your computer usage patterns and learns which applications and files you use most frequently. It also takes into account the time of day and other factors that may affect your usage patterns. Based on this information, Superfetch will load the necessary data into memory in advance, reducing the time it takes for applications to launch and files to open.
Superfetch uses a prioritization algorithm to determine which files and applications should be loaded into memory. It gives priority to the most frequently used files and applications, but it also considers the amount of available memory and the frequency of use. If there is not enough memory available, Superfetch will prioritize the most important files and applications and load them first.
Superfetch can also improve boot times by preloading necessary system files and applications during startup. By preloading these files, Superfetch can reduce the time it takes for your computer to start up and become usable.
Overall, Superfetch aims to provide a faster and more responsive computing experience by anticipating your needs and loading the necessary data into memory ahead of time. However, there are situations where Superfetch may not be beneficial, such as when you have a low amount of available memory or if you frequently use different applications that are not accurately predicted by Superfetch.
In the next sections, we will explore the pros and cons of disabling Superfetch to help you decide whether or not it is the right choice for your specific computer usage.
Benefits of Superfetch
1. Improved system performance: Superfetch helps improve the overall performance of your computer by predicting the applications and files you are likely to use and preloading them into memory. This reduces the time it takes for these programs to load, resulting in faster access to your frequently used applications.
2. Reduced program launch time: By preloading frequently accessed applications and files, Superfetch significantly reduces the launch time of programs. This means that you can open your favorite applications faster, improving your productivity and saving time.
3. Enhanced data access speed: With Superfetch, data access speed is improved as the frequently accessed data is stored in memory. This reduces the need for the computer to fetch data from slower storage devices such as hard drives, resulting in faster data retrieval and improved system responsiveness.
4. Efficient memory management: Superfetch intelligently manages system memory by adapting to your usage patterns. It optimizes memory usage by prefetching data that is likely to be accessed, while also maintaining a balance between memory consumption and the needs of other running applications.
5. Smooth multitasking: Superfetch enhances multitasking capabilities by efficiently utilizing system memory. It prefetches the data required for your active tasks, allowing you to switch between applications smoothly and without any noticeable delays.
6. Improved gaming experience: Superfetch can significantly improve the gaming experience by loading game files and resources into memory ahead of time. This reduces loading times and helps ensure a smoother gameplay experience with reduced stuttering or lag.
Overall, Superfetch provides several benefits that contribute to a more responsive and efficient system, particularly for those who regularly use the same applications or perform resource-intensive tasks.
Potential Drawbacks of Superfetch
- Increased RAM usage: Superfetch aggressively preloads data into RAM, which can lead to a higher usage of memory. This may cause slower performance for systems with limited RAM or when multiple memory-intensive applications are running simultaneously.
- Slower startup times: While Superfetch is designed to improve overall system performance, it may result in longer startup times for some users. This can be particularly noticeable on systems with slower hard drives, as the preloading of data can contribute to a delay in the system fully booting up.
- Potential conflicts with other optimization tools: Superfetch can potentially conflict with other optimization tools or utilities that are designed to improve system performance. This can lead to unpredictable results and may require users to disable Superfetch in order to troubleshoot performance issues.
- Incompatibility with certain applications: In some cases, Superfetch may be incompatible with certain applications or software that have specific memory management requirements. This can result in crashes or errors when running these applications, necessitating the disabling of Superfetch to resolve the issue.
- Increased wear on SSDs: Superfetch can increase the number of read and write operations on solid-state drives (SSDs), potentially leading to faster wear and reducing the lifespan of the drive. While modern SSDs are designed to handle a significant amount of data processing, users with older or lower-quality SSDs may want to disable Superfetch to mitigate this potential issue.
Overall, while Superfetch can improve system performance by preloading frequently used data into RAM, it may have some drawbacks for certain users. It is important to weigh the potential benefits against these potential drawbacks and consider the specific hardware and software configuration of your system before deciding whether to enable or disable Superfetch.
How to Disable Superfetch
If you have decided to disable Superfetch on your Windows system, there are multiple methods you can use depending on your preferences and technical expertise. Here are a few ways you can disable Superfetch:
- Using Services Manager: This method allows you to disable Superfetch using the Services Manager interface.
- Using Command Prompt: If you prefer using the command line, you can disable Superfetch by executing a command in Command Prompt.
- Using Registry Editor: Advanced users can disable Superfetch by modifying the Windows Registry.
- Method 1: Using Services Manager
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
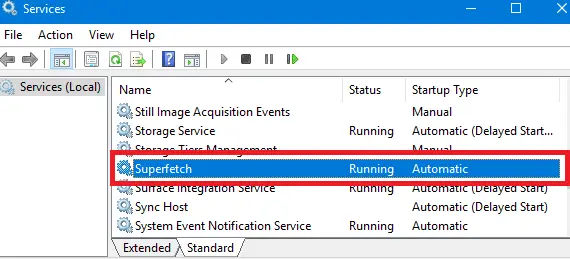
2. Type “services.msc” in the Run dialog box and press Enter.
3. In the Services Manager window, scroll down and locate “Superfetch” in the list of services.
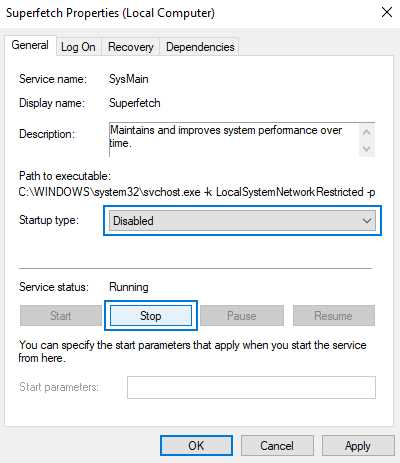
4. Right-click on “Superfetch” and select “Properties” from the context menu.
5. In the Superfetch Properties window, go to the “General” tab.
6. Under the “Startup type” section, select “Disabled” from the dropdown menu.
7. Click on the “Apply” button to save the changes.
8. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
- Method 2: Using Command Prompt
1. Press the Windows key + X and select “Command Prompt (Admin)” from the menu.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
net.exe stop “SysMain”
3. Wait for the command to execute. This will stop the Superfetch service.
4. To disable Superfetch permanently, type the following command and press Enter:
sc.exe config “SysMain” start=disabled
5. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
- Method 3: Using Registry Editor
WARNING: Modifying the Windows Registry can be risky. Make sure to follow the steps carefully and create a backup of your Registry before making any changes.
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “regedit” in the Run dialog box and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
3. In the Registry Editor, navigate to the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
4. Double-click on the “EnableSuperfetch” entry on the right side.
5. Change the value data from “1” to “0” and click on the “OK” button.
6. Close the Registry Editor.
7. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
By following one of these methods, you can disable Superfetch on your Windows system. Disabling Superfetch may improve system performance in certain situations, but it may also affect the overall responsiveness of your system. It is recommended to test the performance impact before deciding to permanently disable Superfetch.
Pros of Disabling Superfetch
While Superfetch is designed to improve system performance by preloading frequently used applications into memory, there are some potential benefits to disabling it:
- Reduced memory usage: Disabling Superfetch can free up memory resources, which can be beneficial if you have a limited amount of RAM. This can allow your system to run more smoothly and prevent it from becoming overloaded.
- Improved boot time: Superfetch can sometimes cause delays during the boot process as it loads applications into memory. By disabling Superfetch, you may experience faster boot times and be able to start using your computer more quickly.
- Prevents potential issues: In some cases, Superfetch may cause compatibility issues with certain applications or drivers. Disabling Superfetch can help to avoid these issues and ensure that your system runs smoothly without any conflicts.
- Increased control: Disabling Superfetch allows you to have more control over which applications are loaded into memory. This can be useful if you prefer to manually manage your system resources or if you have specific applications that you want to prioritize over others.
It is worth noting that while disabling Superfetch can provide these benefits, it may also have some drawbacks. It is recommended to weigh the pros and cons and consider your specific system configuration and usage patterns before deciding whether to disable Superfetch.
Cons of Disabling Superfetch
While there are potential benefits to disabling Superfetch, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- Decreased performance for certain applications: Superfetch preloads frequently accessed data into memory to improve overall system performance. Disabling it can result in slower loading times for certain applications, especially those that heavily rely on accessing large amounts of data from the hard drive.
- Increased disk usage: With Superfetch disabled, the system will rely more heavily on the hard drive to load data, leading to increased disk usage. This can reduce the lifespan of the hard drive and may result in slower overall system performance, especially on systems with slower hard drives.
- Potential compatibility issues: Disabling Superfetch can sometimes cause compatibility issues with certain software or drivers. This can result in crashes, instability, or other issues that may require troubleshooting and resolving.
- Overhead during system startup: Superfetch has a small overhead during system startup as it preloads data into memory. Disabling it can slightly reduce the startup time, but the impact may not be significant and may not outweigh the potential benefits of having frequently used data readily available in memory.
In conclusion, while disabling Superfetch can have some benefits in specific scenarios, it is important to weigh these against the potential drawbacks. It may be worthwhile to experiment with disabling Superfetch on your system and observe the impact on performance, but it is also recommended to consult official documentation or seek expert advice before making any changes to system settings that can affect its stability and performance.
User Experiences with Superfetch
Superfetch, a feature introduced by Microsoft in Windows Vista, is designed to improve system performance by preloading frequently used applications and data into memory. While its goal is to speed up the overall user experience, the results can vary depending on the specific hardware and software configurations.
Some users have reported positive experiences with Superfetch. They claim that it significantly reduces the loading times of their frequently used applications, resulting in a smoother and more responsive system. By preloading these applications into memory, Superfetch ensures that they are readily available whenever the user needs them.
However, not all users have had a positive experience with Superfetch. Some have experienced performance issues and slowdowns after enabling the feature. These users argue that Superfetch consumes too much system resources, causing their system to become sluggish. They have reported that disabling Superfetch improved their system’s performance and responsiveness.
Another common complaint about Superfetch is its impact on system boot times. Some users have noticed that their systems take longer to boot when Superfetch is enabled. This delay can be attributed to the time it takes for Superfetch to analyze and preload the necessary data during the startup process. Disabling Superfetch, in some cases, has reduced the boot times for these users.
It is important to note that the impact of Superfetch on system performance can vary depending on the specific hardware and software configuration. While some users may benefit from this feature, others may experience issues. As such, it is recommended to test Superfetch on your system and monitor its impact on performance before deciding whether to enable or disable it.
In conclusion, user experiences with Superfetch are mixed. While some users have experienced improved performance and responsiveness, others have reported slowdowns and longer boot times. Ultimately, the decision to enable or disable Superfetch should be based on individual system performance and user preferences.
FAQ:
What is Superfetch and what does it do?
Superfetch is a feature in Windows that helps to speed up system performance by preloading frequently used data into memory. This means that when you open an application, the data it needs is already in memory, reducing the amount of time it takes for the application to load.
Does Superfetch consume a lot of system resources?
Superfetch does use some system resources, such as CPU and memory, to monitor and analyze which data should be preloaded into memory. However, it is designed to prioritize background tasks and give priority to user-initiated tasks, so it should not significantly impact system performance.
Can disabling Superfetch improve system performance?
Disabling Superfetch may improve system performance in certain scenarios, especially if you have a low amount of RAM or an older, slower hard drive. However, for most users with modern hardware, the performance improvement from disabling Superfetch is likely to be minimal or even negligible.
Does Superfetch have any negative effects on system performance?
In rare cases, Superfetch may cause high disk usage, especially if it is constantly analyzing and preloading data. This can lead to a decrease in overall system performance. However, this is not a common issue and can usually be resolved by restarting the Superfetch service or updating your Windows version.
Can disabling Superfetch affect the overall user experience?
Disabling Superfetch is unlikely to negatively affect the overall user experience, especially for users with sufficient RAM. However, some users may notice a slight increase in application launch times, as the data will no longer be preloaded into memory. This increase in launch times is typically minimal and may not be noticeable in day-to-day usage.
Is there any specific scenario where disabling Superfetch is recommended?
Disabling Superfetch may be recommended in scenarios where you have a very low amount of RAM, such as 2GB or less, or if you are using an older hard drive with slow read and write speeds. In these cases, the performance benefit of disabling Superfetch may outweigh the potential benefits of having frequently used data preloaded into memory.
How can I disable Superfetch on my Windows system?
To disable Superfetch, you can open the Services application by pressing Windows + R, typing “services.msc”, and pressing Enter. From there, locate the “Superfetch” service, right-click on it, and select “Properties”. In the properties window, change the startup type to “Disabled” and click “Apply” and “OK”.